News Story
Wood Cathode Architecture Continues to Make Headlines
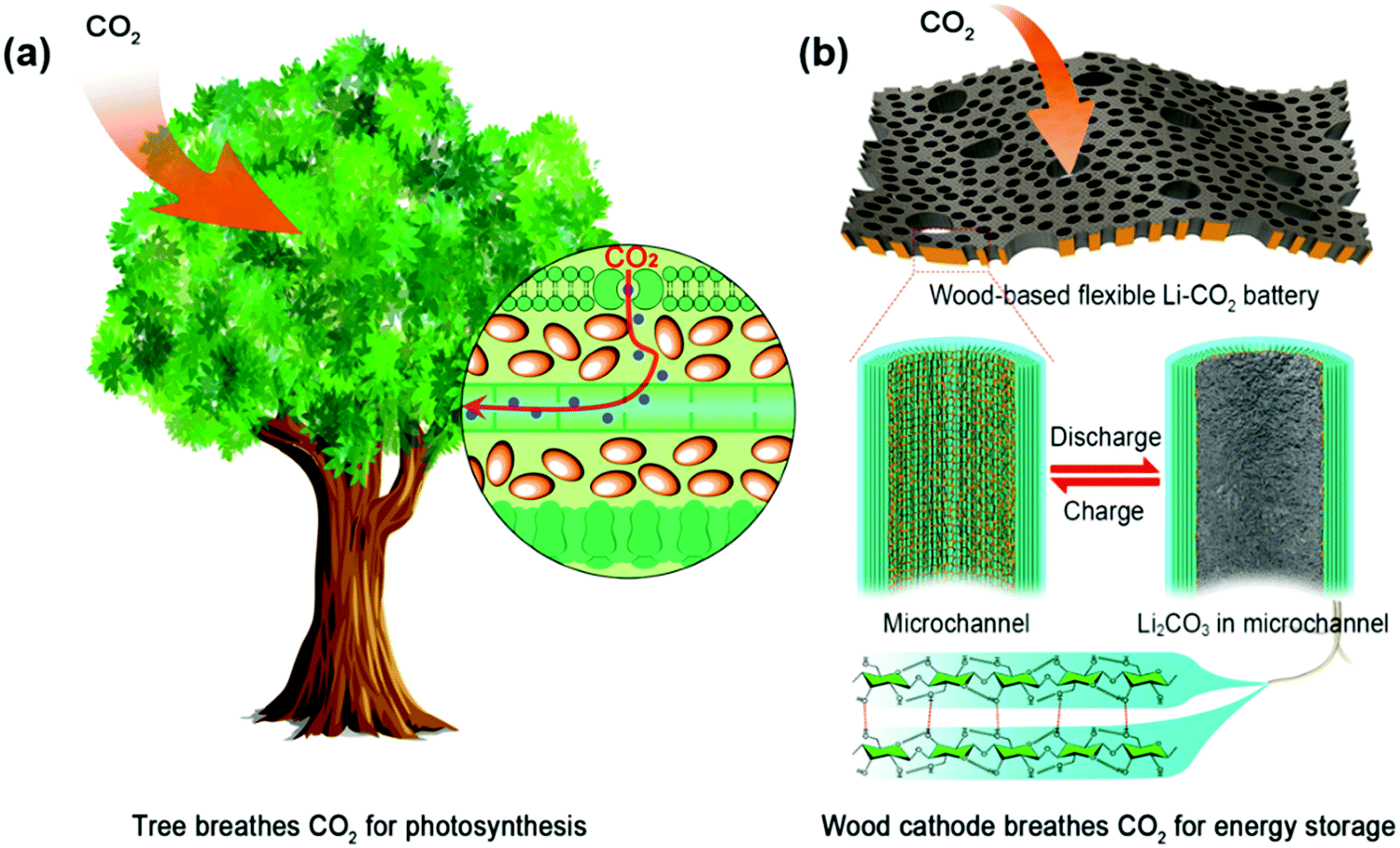
The Li–CO2 battery is considered a promising platform for CO2 capture, with its ability to utilize the captured CO2 for energy storage. However, the Li–CO2 battery still suffers various inadequacies, including the slow kinetics of CO2 reduction, the high charge/discharge hysteresis, the ultra-stable discharge product, and the slow transport of CO2 gas and electrolyte. To overcome this challenge, Liangbing Hu, director of the Center for Materials Innovation at UMD, constructed a battery using readily available, porous, holey pieces of wood as the electrodes. Wood is plentiful, low cost and lightweight, offering great potential in energy storage devices.
This study was published on Energy & Environmental Science and reported by BBC Future.
Published July 27, 2020